Effective compliance reporting is a vital part of being able to demonstrate compliance with today’s strict regulations. However, proper compliance reporting is difficult to do effectively without the proper tools, practices, and processes in place. In this blog, we’ll explore how you can improve your internal compliance reporting and better align yourself with GDPR, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and more.
What is Compliance Reporting?
Compliance reporting refers to the process by which an organization submits tangible evidence that its compliance and security posture adhere to internal and external audit standards. Compliance reporting is proof of an organization’s adherence to relevant corporate or legal guidelines and directives. The auditors normally maintain it updated and submit it as part of their evidence to confirm the compliance status level and quality.
Compliance reports are strategically valuable because they convey an organization’s dedication to the pursuit of operational excellence and integrity, and this opens the way for long-term growth and stability in a regulatory environment that is changing at high speed. The main aim is to present a brief, factual account of the organization’s state of compliance, highlighting both strengths and weaknesses.
What are the Types of Compliance Reporting?
The primary types of compliance reporting that certify compliance for specific functions are listed below.
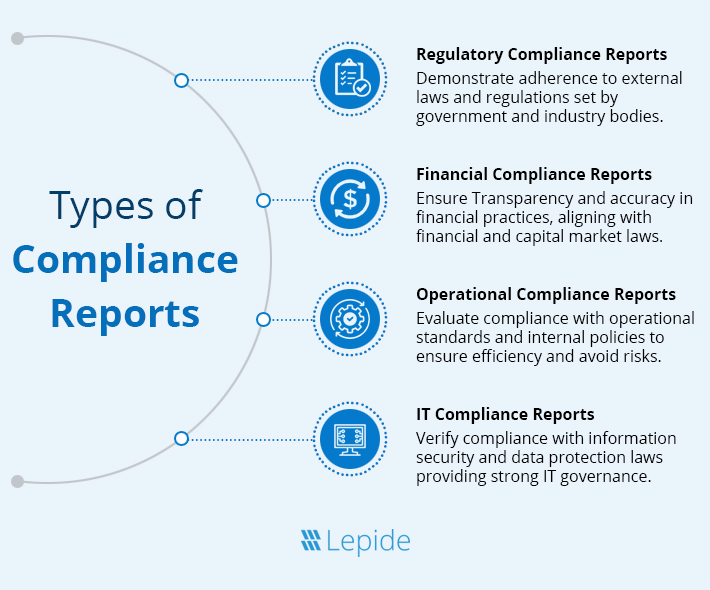
- Regulatory Compliance Reports: The regulatory compliance discusses adherence to applicable laws and industry rules, such as PCI DSS for payment card industry standards, HIPAA for protection of healthcare data, which protects sensitive patient health information in the US, and GDPR for data protection. These reports are vital in ensuring that organizational procedures adhere to legal guidelines, protecting the firm from potential fines and violations. Regulating bodies oversee them as outside compliance in making decisions on compliance status. They may vary depending on the industry, applicable laws, and geographic sector.
- Financial Compliance Reports: The phrase “financial compliance reports” refers to the compliance of an organization with regulations overseen by capital markets, the financial sector, and accounting principles. They scrutinize the accuracy of financial reporting and transactions, making them accountable and transparent as per financial standards and regulations. They are responsible for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring the financial health of the company. To build confidence in the financial well-being of the organization and the adequacy of internal controls, financial statements such as the income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, etc., are analyzed. IFRS (international accounting financial reporting standards), GAAP (standardized framework of norms of financial accounting), and Money Laundering Reports (tracking and reporting suspicious transactions of funds) are a few.
- Operational Compliance Reports: In regard to compliance standards of the corporate level, operational compliance reports analyze the effectiveness of business processes. Since they stick to standard norms, internal stakeholders whose aim is to streamline business operations will not be able to do without such reports. These operational compliance reports address topics such as: Quality Management System to maintain product and service quality consistency, Workplace safety standards, environmental laws, and EHS (Environmental, Health, and Safety) audits are some of the supply chain audits that measure suppliers’ compliance with contractual and statutory obligations. Their primary goal is to record an organization’s commitment to upholding operating standards, as well as compliance with internal policies and industry standards.
- IT Compliance Reports: The IT compliance reports highlight fair IT governance as well as conformity to data security and information privacy legislation. The reports center around an organization’s IT infrastructure as well as the data security policies since the globe is still increasing because of technology. Examples include: The ISO/IEC 27001 describes the requirements for developing, implementing, and maintaining an information security management system, and the SOC (System and Organizational Controls) report assesses the adequacy of internal controls over financial reporting and data protection.
Which Types of Organizations Requiring Compliance Reporting?
Not all industries are the same when it comes to IT security requirements, with many industries requiring stricter compliance reports and standards than others. Such industries include:
- Healthcare: Compliance reporting is essential in the healthcare industry to ensure confidentiality of patients, maintain data protection, and deliver quality care. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandating the protection of patient health information is one of the important legislations. Both of the two parts of HIPAA necessitate compliance reports. The HIPAA Security Rule necessitates specific procedures for managing health information electronically, while the HIPAA Privacy Rule establishes standards for safeguarding medical records and individual health information. Regular risk assessment, implementation of security controls, and notification of any violation to the respective authorities are mandatory for healthcare businesses. Furthermore, adherence to the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) is necessary to ensure that laboratory testing is of quality.
- Financial Services: The financial institutions function under strict regulation to ensure the integrity of the financial system. Reporting compliance in this sector is following legislation like Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), under which there are proper financial disclosures, PCI DSS data security requirements for any enterprise dealing with processing, storing or transmitting credit card data. · Periodic audits, internal controls evaluations, and prompt reporting to authorities like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) are the mandatory aspects of financial compliance.
- Manufacturing: There are various safety and environmental regulations manufacturing businesses need to comply with. Manufacturing businesses are also required by several cybersecurity legislation and guidelines such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and the IEC standards to be compliant with. Thus, their reports on compliance are to declare compliance with such laws. Manufacturers must further report the methods through which risky products are transported and used, and attest to proper labelling and handling guidelines being established.
- Information Technology and Cyber Security: Data security and cybersecurity are specific compliance issues in the information technology sector. Installing access controls, performing regular security audits, and alerting the proper authorities to data breaches are all part of compliance reporting. Organizations can better limit and address cybersecurity threats by adhering to recommendations like the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework.
What are Compliance Reporting Examples?
- Financial Statements: The yearly reports that are filed with financial authorities reporting income, expenditure, and financial situation. The complete records prove the correctness of financial statements to show the actual financial status of business.
- Risk Management: This refers to the identification, measurement, and management of potential risks that may adversely affect an organization’s goals. Analysis of the various risks such as credit risks, market risk, operational risk along with steps taken to overcome the risks.
- Cybersecurity Incident Reports: Records of data breaches or cyber attacks that have been reported to appropriate authorities. This would also involve reports of training schemes for employees so that they can be informed of compliance requirements and best practices.
- Health and Safety Reports: Reports would contain HIPAA compliance emphasizing administrative, technical, and physical safeguards effectiveness in safeguarding patient health information(PHI). These are privacy, security, breach notifications etc. and are evaluated along with policies, procedures, and controls.
- Data Protection Impact Assessment Reports: The analyses are made for complying with data privacy legislation such as GDPR. GDPR compliance reports feature a description of data privacy initiatives taken for the protection of EU citizens’ personal data.
What are Compliance Reporting Requirements?
Understanding the standards for compliance reporting directs a few requirements and shapes the format of your compliance report.
-
- Collection of Data: The data collection requirement is the process of gathering all records, documents, and evidence of the company’s compliance efforts. The major reason for the requirement is to have a set of data that provides a comprehensive picture of the compliance environment without leaving anything behind. Identification and involvement of key stakeholders are critical, and it seems to happen in tandem with data collection. Such stakeholders cross organizational levels and departments, including those that directly oversee or are within the compliance program.
- Thorough Compliance Audit: The primary run of a compliance stream is a thorough compliance audit which is the process that demands detail, discipline, and strategic planning. It is a process of a thorough review of the systems, procedures, and controls of an organization to determine if they are compliant with the applicable regulatory requirements and security standards. A thorough compliance audit is more than a cosmetic review and includes a comprehensive review of data handling practices, internal controls, and the efficacy of the compliance program in its present configuration. The findings from the audit provide the foundation for the compliance report, providing a fact-based foundation to determine deficiencies, categorize risks by severity, and prioritize corrective action. By performing a thorough compliance audit, organizations empower themselves with the right information required to bolster their compliance position, adopting a reactive compliance approach and an active and strategic compliance approach toward regulation demands and risk.
- Analyzing Findings: After the compliance audit is done, critical evaluation of the data collected is emphasized, which is critical in determining non-compliance and their root causes leading to such deviations. It is more helpful to have an explicit understanding of the findings of the audit and is conducive to a team solution approach to addressing the compliance gaps established. This collaboration is central to developing effective action plans tailored to solve the root cause of non-compliance problems, thereby improving the overall compliance profile of the organization. This analytical process forms the basis for creating such targeted action plans. It allows for careful review of the nuances of each issue identified, and this enables chief compliance officers and compliance managers to develop accurate correction measures in proportion to the organization’s risk management priorities and needs as well as regulatory requirements. By such close scrutiny, companies are best placed to turn issues of compliance into a chance to enhance compliance systems.
- Developing Action Plans: This stage begins immediately from the detailed review of audit findings and determined non-compliance issues. The action plans should be well detailed, specifying clear remedial actions, assigning responsible individuals, and having clear timelines for implementation. This would provide accountability, and enables tracking of progress towards compliance improvements. This would involve short term solutions and blending it with long term strategies. This can include revising or developing thorough policies and procedures, strengthening internal controls, and having effective training programs for employees to build a culture of compliance within the organization at every level. Another method of building action plans is by using automation tools, as well as compliance management software. It would automate processes and decrease errors caused by humans while notification systems providing real-time checks and rapid response to possible compliance violations.
- Compilation of Report: At this stage, correctness, coherence, and clarity must be given priority to overcome the expectations and requirements of regulatory authorities and stakeholders. To produce an overall report that correctly reflects the organization’s compliance status and future direction, the information, audit results, evaluations, and action plans need to be integrated. Seamless transition between every segment of the report should produce a clear data flow that enhances comprehension. One of the ways to simplify the process and reduce costs is to develop or utilize a compliant report template. All statements and information in the report must be checked for accuracy and pertinence so that the final product is a true reflection of the company’s commitment to compliance excellence.
How Lepide Helps with Compliance Reporting
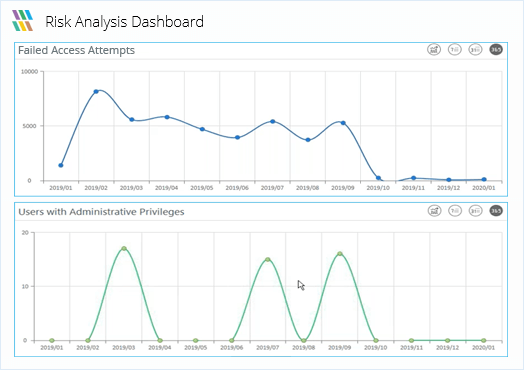
Lepide Data Security Platform simplifies compliance reporting with pre-configured reports, real-time alerts, and risk analysis dashboards that are aligned with major compliance requirements, such as GDPR, PCI, HIPAA, SOX, ISO, and others. Through user-friendly risk analysis dashboards, real-time monitoring, auditing, and alerting, Lepide offers comprehensive insight into changes occurring across important systems and sensitive data, permissions, configurations, and vital infrastructure. On-demand reports assist the compliance team in delving deeper into the threat surface area, over-exposed regulated data, and current data threats.
To learn more about how Lepide can improve compliance reporting, download a free trial now or arrange a demo with one of our engineers.