File servers hold your documents, people rely on, code that runs the business, backups you hope you never need, and the occasional mistake you definitely need to explain. You need a tool that logs access, shows changes, warns on risky moves, and helps with compliance reports.
Below are 10 File Auditing and File Server Monitoring software that do this well, listed with a short note on what they do best and a source so you can check details.
- Lepide Auditor for File Server
- Netwrix Auditor
- IS Decisions FileAudit
- Varonis DatAdvantage
- ManageEngine DataSecurity Plus
- SolarWinds Access Rights Manager (ARM)
- AuditSphere
- Quest Change Auditor
- Vyapin NTFS Change Auditor
- Splunk Enterprise + Splunk ES
Top 10 File Auditing and File Server Monitoring Software
1. Lepide Auditor for File Server
Lepide is the tool you call when someone yells “where did that file go?” in a meeting. It turns raw Windows events into readable answers about who created, changed, copied, moved or deleted files, and it shows permission changes in a way auditors can actually follow. You get prebuilt reports and quick alerts so investigations stop being a scavenger hunt.
It’s fast to stand up and practical to use. Teams like it because it focuses on the day-to-day questions, who did what, when, and from where — without trying to be every security product you will never finish configuring.
Key Features:
- Real-time file access and change audit.
- Permission comparison and reports.
- Prebuilt compliance templates.
- Alerting on suspicious activity.
- Simple investigator-friendly UI.
2. Netwrix Auditor
Netwrix slices through Windows event noise and gives you plain-language records of file activity and permission changes. It’s made for environments where audits happen a lot and management expects consistent, repeatable reports rather than a pile of raw logs.
If you have a big estate and need lots of report templates and long-term history, Netwrix is a safe choice. It can feel heavyweight for tiny shops, but when you need consistent audit output across many servers, it pays off.
Key Features:
- Normalizes Windows file events.
- Large library of compliance reports.
- Change history and alerting.
- Scalable collectors.
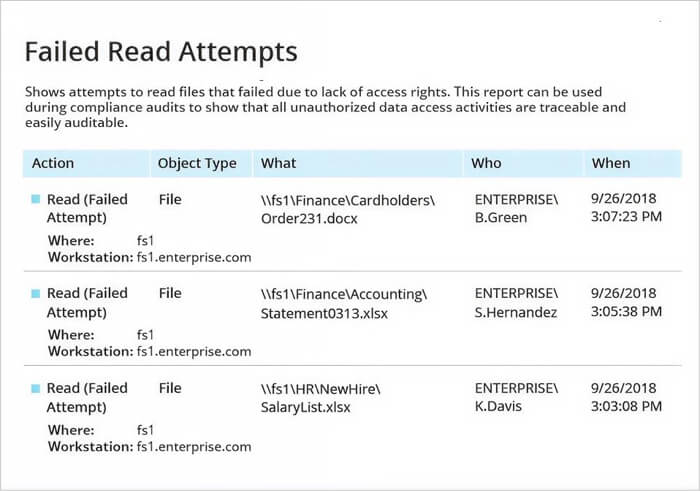
3. IS Decisions FileAudit
FileAudit does one thing and does it well. It tracks file opens, edits, copies, deletes and failed access attempts across Windows servers and common cloud drives, and presents a clear searchable trail. Setup is usually quick and low-friction.
Because it stays focused on file access, it’s a good fit for IT teams that want clean audit trails without the overhead of a full-blown security suite. If your goal is fast answers during incidents, FileAudit will give them.
Key Features:
- Agentless option, Windows and cloud connectors.
- Real-time alerts and searchable audit logs.
- Simple dashboards.
- Fast install.
4. Varonis DatAdvantage
Varonis takes a birds-eye view of data exposure. It maps where sensitive files live, shows who has access, and watches how people actually use that access so you can spot risky behavior rather than just raw events.
It’s not the quickest to set up and it is pricier, but for organizations worried about over-shared data or insider risk, Varonis gives context that simple file logs do not. Use it when reducing data exposure matters as much as auditing access.
Key Features:
- Data mapping and classification.
- Behavior analytics and anomaly detection.
- Permission and exposure reports.
- Forensics-ready audit trails.
5. ManageEngine DataSecurity Plus
This is a practical combo of file auditing, file integrity checks and sensitive data discovery. It tracks who accessed or changed files, checks integrity for critical files, and warns when risky patterns appear, like mass deletes or unusual access times.
It’s a good mid-market pick when you want useful features without enterprise sticker shock. Expect a lot of capability for the money, but you’ll want to tune alerts so your inbox does not explode.
Key Features
- Real-time file access auditing.
- File integrity monitoring.
- Sensitive data discovery.
- Compliance-ready reports and alerts.
6. SolarWinds Access Rights Manager (ARM)
ARM focuses on permission clarity. It shows who has access, how that access was given, and surfaces stale accounts and overgrown groups. It also collects basic file activity so you can pair access rights with actual behavior.
Teams usually start with ARM to get control of permission sprawl before running automated cleanups. It’s straightforward in AD-heavy shops and helps cut down “I don’t know why they can access X” conversations.
Key Features
- Permission analysis.
- AD and file server connectors. Compliance reporting.
- Provisioning and deprovisioning workflows.
- Activity logging.
7. AuditSphere
AuditSphere is an open-source file server auditing and monitoring project that works across Windows and Linux. It uses lightweight agents on file servers to capture file events and a Django web app as the server component to store logs and present the UI. AuditSphere records adds, removes, modifications, renames, moves, ACL changes, owner changes, and more, and it produces human-readable reports and dashboards for investigations. It’s a practical pick when you want an open solution that you can host and extend, and when you prefer agent+server architectures for real-time file monitoring.
Key Features
- Agent + server architecture (agents run on file servers, server is a Django web app).
- Tracks file add/remove/modify/rename/move, owner and ACL changes.
- Records user, timestamp, and client IP for each event
- SMB protocol support (Windows file shares) and Linux coverage.
- Generates HTML reports and supports command-line or interactive installs.
8. Quest Change Auditor
Change Auditor turns messy Windows events into a readable timeline so you can see the sequence of actions that led to an incident. It reports who did what and gives original vs current values to speed troubleshooting.
If your environment is Microsoft-centric and you need clear change timelines for investigations, this tool is built for that kind of work. It’s not about data classification or behavior analytics, it’s about accurate change history.
Key Features
- Real-time change auditing.
- Detailed event context and timeline views.
- “Who did what, when” forensic logs.
- Integrations with Microsoft stacks.
9. Vyapin NTFS Change Auditor
Vyapin’s NTFS Change Auditor is a commercial file access auditing tool built for Windows file servers. It reads Windows Security event logs in real time, stores a history of NTFS changes in a database, and produces a wide set of NTFS-focused reports such as “who accessed what,” permission changes, ownership changes, and share activity. It is aimed at teams that need straightforward, Windows-native file access auditing with prebuilt reports for compliance and forensic review. The product is delivered as a Windows installer and stores collected audit history in SQL for long-term retention.
Key Features
- Real-time collection from Windows Security event logs for NTFS shares and files.
- Rich set of NTFS reports: file/folder changes, permission changes, ownership change, “who accessed what.”
- Real-time alerts and historical change storage in SQL for forensic analysis.
- Supports a wide range of Windows Server and desktop OS versions.
- Designed for compliance (HIPAA, SOX) and detailed forensic reporting.
10. Splunk Enterprise + Splunk ES
Splunk itself is a log indexing engine. Feed it file server events and Splunk becomes a powerful auditing and investigation tool. Splunk ES adds security workflows, correlation and incident-focused views to help surface suspicious file activity among other signals.
This is a top pick when you already run Splunk or need deep search and correlation. The tradeoff is cost and the need to design what to ingest, because file read logs can balloon quickly if you do not filter smartly.
Key Features
- Raw log indexing and fast search.
- Custom dashboards and correlation.
- Splunk ES for security use cases.
- Alerts and automated workflows.
| Tool | Deployment mode | Best fit | Cost Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lepide Auditor for File Server | Collector/Server install | Fast audit, compliance | Mid |
| Netwrix Auditor | Collector | Repeatable audits | Mid |
| IS Decisions FileAudit | Agenless/Lightweight | Small-mid shops, fast setup | Low-Mid |
| Varonis DatAdvantage | Collectors+engines | Data exposure risks and analytics | High |
| ManageEngine Data Security Plus | Collector/Agent | All round file audit+FIM | Mid |
| SolarWinds ARM | Collector/AD connectors | Permission visibility+Basic audits | Mid |
| AuditSphere | Agent+Server (Open-source) | Open-source file server auditing for Windows and Linux | Low (OSS) |
| Quest Change Auditor | Collector | Microsoft change forensics | Mid |
| Vyapin NTFS Change Auditor | Collector/Server Install (Windows) | Windows NTFS file server auditing, compliance and forensics | Low-Mid |
| Splunk + ES | Forwarders/Indexers | Deep search and correlation | High |
Conclusion
File auditing tools fail when they try to impress instead of explain. The best ones help you answer simple questions under pressure. Who accessed this? What changed. When it happened. Why does it matter?
If you want clean answers and audit-ready reports, tools like Lepide and Netwrix do that job well. If you care about data exposure, Varonis adds context. If you want full control and flexibility, open-source tools demand more work but offer freedom.
FAQs
1. Which file events should I log to balance visibility and cost?
Start with writes, deletes, renames, and permission changes. Those actions usually matter most for investigations and compliance. Log reads only if a specific use case needs it, because read logging multiplies event volume quickly.
2. Agent vs agentless. Which deployment model should I choose?
Use collectors or agentless methods for easier rollouts and smaller server footprints. Choose agents when you need deeper endpoint visibility or file integrity checks that require local monitoring. Hybrid deployments are common.
3. How long should I keep file audit logs for?
Retention depends on regulation and your investigation needs. For basic incident response, 90 days is common. For compliance like SOX, HIPAA or PCI, retention can be one year or more. Check your industry rules and plan storage accordingly.
4. How do I run a proof of concept for a file auditing tool?
Pick two representative servers. Enable the events you plan to keep. Measure event volume, check alerts for false positives, and test sample questions like who deleted or moved a file. Evaluate how easy it is to produce audit reports and how quickly your team can find answers.