Authentication in Active Directory (AD) is a crucial component of the intricate network security environment, protecting sensitive information and guaranteeing authorized access inside enterprises.
What is Active Directory Authentication?
Active Directory Authentication is a Windows-based system that verifies and permits users, endpoints, and services to access Active Directory. Through this system, you may confirm the identity of individuals and devices trying to connect to your network. It guarantees that only those who are permitted can access particular resources. The creation of Active Directory Authentication was prompted by the need for a more efficient and centralized approach to managing user identities, access rights, and network resources in growing and increasingly complex IT surroundings.

What are The Key Components of Active Directory Authentication?
Now let’s talk about the essential elements of Active Directory authentication:
- User Authentication: A username and password combination serves as Active Directory’s main means of user authentication. When the user attempts to log in, the information stored in Active Directory is checked with the credentials they entered. If their credentials match, the user is granted access. Active Directory supports other authentication components to increase security, such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), which requires users to provide various forms of identification. For this, a temporary code that was sent to a mobile device or created by an authentication app is required.
- Computer Authentication: The computers that are part of an Active Directory domain must authenticate, just like users do. Every computer in the domain has a computer account, which is a unique identifier. The computer authenticates itself to Active Directory throughout the authentication procedure. Protocols such as the Kerberos authentication protocol provide secure communication between computers and Active Directory. Kerberos employs tickets to authenticate machines and users without sending private data across the network.
- Service Authentication: Active Directory facilitates user and machine authentication and authorization for several services, including file servers, printers, and databases. This guarantees that certain services are only available to authorized entities. Service Principal Names (SPNs), which permit each instance of a service to be uniquely identified, are frequently used in service authentication. Active Directory uses SPNs to make sure the service-seeking authentication is legitimate and has the required authorization.
What is the difference between AD Aauthentication and Authorization?
| Particulars | AD Authentication | AD Authorization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authentication is just ensuring that someone is actually who they say they are a type of identity check for a user. | Knowing the access level of a user and giving access permission based on that is called authorization. |
| Purpose | The objective is to allow only legitimate users access to the system by excluding any shady figures whose identities can’t be confirmed. This is really important to keep that unauthorized user out. | Authorization is the mechanism to control user access to resources and they can see only those resources which they are authorised to access. |
| Mechanism | Most authentication methods work by checking a user’s credentials before allowing them into the system. These credentials might include a one-time pin (OTP) sent to their mobile device, answers to security questions, or their login details like username and password. | According to the roles or permissions, ACE can be allowed or denied. One of the mechanisms used in computer systems to control access is authorization and there are several ways of implementing it, and one is by using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). |
| Methodologies Used | Credential-based authentication methods compare the credentials provided by the user against a record in a database. If everything matches perfectly, the user is granted access to their account. | RBAC is a popular approach to authorization. Instead of tying permissions directly to individual users, RBAC associates them with specific roles. This way, users can only access the information necessary for their job functions, keeping everything secure and organized |
What are The Types of Active Directory Authentication?
Active Directory Authentication supports two types of authentication::
- Kerberos Authentication: A kerberos authentication is mainly used to put into place single sign-on and ensure secure data sharing on networks. Kerberos can also help to provide effective access control whereby only authenticated and authorized personnel are granted access to resources on the network. Authentication and verification of user’s identity is done by using symmetric-key cryptography together with a key distribution center (KDC). At the first stage of multi-level Kerberos authentication, the client knows that a service request is to be made on the user’s behalf. The services the server is supposed to access are listed below. After authentication, Kerberos retains the unique ticket belonging to the end user machine. Instead of searching for a password, a Kerberos-aware service searches for the ticket. The domain where KDC is accepted as authenticating a host, user or service is described as a Kerberos realm. This is the domain where the kerberos authentication takes place.
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP): LDAP, as introduced in the early 1990s, has been a fundamental part of most networks communications over the last few decades and allows communication with different directory services. As an example, servers communicate with AD and other directory services using a language known as LDAP. Communication between clients and servers is simplified through client and server request responses as well as data formatting. Binding to an LDAP directory requires a series of steps to be executed in order to complete a request. The procedure connects a user to a server using LDAP. The LDAP server processes the user’s request for pre-defined information, like user credentials, using directory services before passing to the client. LDAP dispenses the client, granting control back to the client after the process is completed from the server.
Best Practices for Active Directory Authentication
To maximize the security and efficiency of Active Directory authentication, consider implementing the following best practices:
-
- Robust Password Policies: Establishing a robust password policy is among the best practices for active directory authentication. Using parameters like password length and complexity requirements, Active Directory enables the definition of fine-grained password policies. NIST has a few rules, such as the requirement that passwords include at least eight characters when created by a human and six characters when created by an automated system. One strong password should be used by the user, as this is thought to be more effective than changing weak passwords frequently. The company should spend money on a password manager that helps customers create secure, one-of-a-kind passwords without adding to the helpdesk’s workload due to frequent account lockouts.
- Extra Layer of Authentication: Security is increased with multi-factor authentication, which asks users to authenticate using two or more different ways, including a code from a hardware or software token or SMS message, biometric authentication, or push notifications to mobile devices. Scalability, usability, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure—including Active Directory—are all factors to take into account. When creating multi-factor authentication protocols, it is important to take into account the roles, groups, and specific security requirements of users. when all privileged accounts, certain programs, or remote access requests need multi-factor authentication.
- Backup and Disaster Plan: If Active Directory is affected by a disaster or outage, the company’s operations could be severely hampered. Using Active Directory Authentication’s disaster recovery plan can help guarantee company continuity in the case of an emergency. Ensure that methods for backup and recovery, failover and failback, and communication and notification are included. Processes for backup and recovery are tested, and backup data is stored overseas. Regularly create backups of Active Directory. Active Directory backup is one of the built-in backup capabilities of Windows Server. AD data can be backed up along with other system states using the “Windows Server Backup” application. Other backup software designed specifically for Active Directory, however, offers greater flexibility and capabilities. Ensure that the backup data is stored securely. This includes protecting backup media from physical damage, restricting access to backup files to authorized personnel, and encrypting backup data. Make a note of the Active Directory backup procedures, including the schedule for the backup, the requirements for retention, and any other environment-specific factors.
- Control Access Rights: Security groups are the suggested method of resource access control to optimize the security and effectiveness of Activity Directory Authentication. Assign permissions to security groups and then add each user to the relevant groups, rather than giving access rights to user accounts one at a time. Only the permissions required for the users to function should be granted. This is referred to as least privilege access implementation. Additionally, strictly adhere to the least privilege paradigm, granting each user just the minimal amount of access required to finish their duties. Keep a careful eye on any changes to security group membership, particularly for those with the authority to view, alter, or delete sensitive information. Disabling accounts for departing employees right away is one of the procedures that should be put into place.
- Auditing and Monitoring: It is thought to be among the most important aspects of verification. The configuration of audit policies must take into account the particular security and compliance requirements of the organization. Consider using automated solutions to generate audit reports on a regular basis to monitor compliance, demonstrate due diligence, and identify trends or patterns in directory activity. To identify any strange activity or dubious changes, audit logs generated by Active Directory should be examined on a regular basis. Consider implementing a real-time monitoring system that will promptly notify users of significant security events and react immediately to possible Active Directory risks.
- Secure Domain Controllers: One Active Directory authentication technique that guarantees data encryption and authentication while safeguarding network traffic between domain controllers is Internet Protocol Security (IPsec). Additionally, to encrypt data transferred between domain controllers and clients, configure SSL/TLS for the LDAP connection in Active Directory. Ideally, domain controllers should be situated in a controlled, secure environment. Implement network and physical security measures to safeguard these vital servers.
- Configuration of Group Policy: Administrators may efficiently manage Active Directory Authentication settings and set domain security parameters by using Group Policy. Because it gives centralized management over security settings, it makes it easier to enforce consistent policies across all users and devices. Group Policy can significantly increase an administrator’s Active Directory environment’s security. Achieving a balance between strong security and a smooth user experience also requires fine-tuning Group Policies. Achieving a successful Active Directory deployment requires ensuring that policies function properly without placing an undue strain on users.
If you like this, you’ll love thisActive Directory Cleanup: Best Practices to Keep AD Clean
How Lepide Helps Secure Active Directory
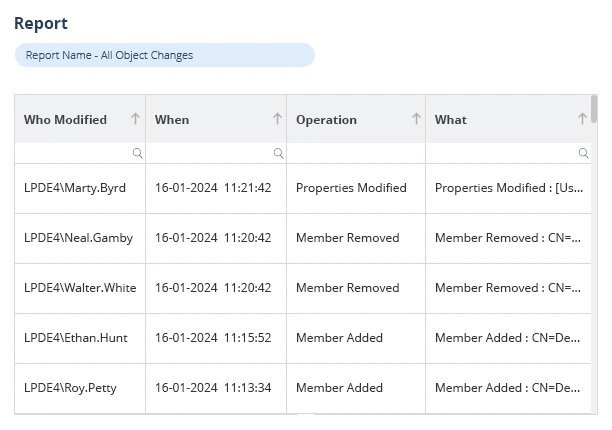
Lepide Active Directory Auditor helps enterprises achieve and maintain Active Directory security and compliance by providing them with complete access to Active Directory configurations and object modifications. Our Active Directory audit tool generates comprehensive audit reports and keeps track of all changes and alterations occurring within Active Directory. By offering data on admin users, inactive users, non-compliant passwords, and misconfigurations, the Lepide auditing tool improves visibility and shows a dedication to lowering overall security risk inside your Active Directory.
If you want to know more about how Lepide helps in Active Directory Auditing, contact one of our engineers to schedule a demo or download a free trial!