Microsoft 365 uses its friendly interface to shield sophisticated permission management, which poses security threats to users who don’t understand or fail to control the system. Administrative visibility of hidden permissions in Microsoft 365 environments remains limited.
Microsoft 365 hides permissions unintentionally due to its complex nature and automatic inheritance processes combined with regular structure changes within organizations. Security professionals now recognize “permission sprawl” as an outcome of growing permission inconsistencies between organizations during their developmental phases.
Why Hidden Permissions Matter
The improper handling of hidden permissions leads to critical security issues:
Security Vulnerabilities
An unknown set of access paths allows improper users to access sensitive data, creating significant threats of information leaks that remain unspotted until a breach is detected. The development of these security vulnerabilities originates from administrative permission accumulation and non-monitoring of changes performed by administrators. Data breaches resulting from unauthorized access through hidden channels lead organizations to deal with compliance-related risks in addition to competitive business losses.
Compliance Failures
Every company under strict regulatory mandates, such as financial organizations, health care institutions, and law firms, keeps compliance in mind and needs strong documentation as well as enforcement for access control systems to prevent regulatory violations. All organizations that operate within GDPR, HIPAA, and financial sector regulations need to monitor access tracking of sensitive data as stated in their governing requirements. Organizations face major financial and reputational consequences because hidden permissions violate compliance efforts, which results in audit failures along with regulatory penalties.
Compliance Failures
Internal staff risks increase dramatically even though security teams focus mainly on outside attacks, because hidden permissions provide unauthorized access routes to internal workers. Organizations risk substantial system damage because they do not track or monitor permissions, which allows attackers to achieve greater system impacts using compromised user accounts. The undisclosed paths through which unauthorized operations take place remain undetected because they create dark areas in which data theft, along with data modification, occurs without triggering standard security monitoring systems.
Governance Challenges
Unidentified backdoor access points make any security policy, regardless of strength, ineffective because organizations cannot fully monitor their systems. Organizations fail to detect security architectural damage from essential permission gaps, though they believe to have proper data governance in place. Organizations maintain false security perspectives about their status because of an incorrect perception between actual reality and perceived conditions, which results in delayed breach response until cases become too severe.
Common Sources of Hidden Permissions in Microsoft 365
SharePoint’s Folder Permission Misconception
SharePoint behaves differently from typical file systems because it constructs an alternative structure for folders and their enclosed content. The standard file system enables administrators to set permissions across folders since this automatically extends to each item contained within them. SharePoint follows a sophisticated modeling system that creates unexpected security breaches in this fundamental element of permission management.
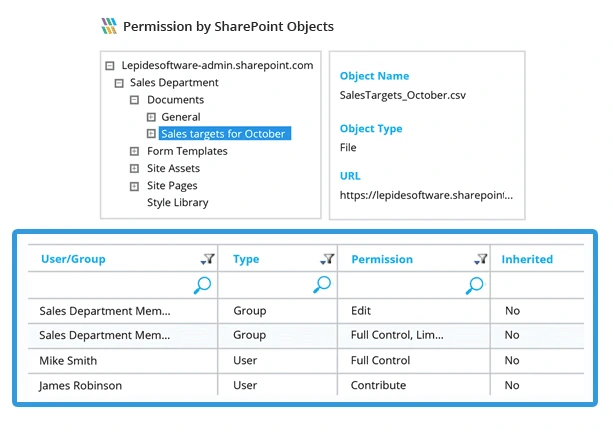
Most administrators apply folder-based permissions with the mistaken belief that they have established complete security zones. SharePoint allows files to operate with separate permission configurations at the individual file level, which might break folder-level control even though there are no visible warnings. Multifaceted document libraries with thousands of documents arranged in multiple folders expose alarming security gaps because administrators expect their permissions to cover the entire collection, but they do not.
Group Membership Complexity
Microsoft 365 provides enhanced group management, which generates permission tiers that prove challenging to track. The inheritance of access rights through multiple group levels creates severe complexity during permission tracking since these additional levels become invisible to tracking systems. The complex group organization makes access rights propagate through multiple levels, so they become difficult to determine during basic permission evaluations.
The dynamic group membership function of Entra ID delivers automation power, which generates changing permission structures that exceed the effectiveness of traditional point-in-time access reviews. The system modifies group affiliations automatically based on user attribute modifications, thus potentially enabling or disabling accessibility through administrative default procedures. The constantly changing group memberships pose difficulties for maintaining precise permission mappings because organizational changes result in frequent movement of members.
Groups that include external collaborators might provide extensive access due to inheritance rules, which leads to unintentional information exposure for outside parties. Data exposure vulnerabilities develop unnoticed during standard access reviews because external members of groups acquire broad resource accessibility when included in multiple resource access systems.
SharePoint’s Broken Inheritance Model
The permission inheritance structure of SharePoint stands out for its flexibility, although it produces major visibility issues. The function of broken inheritance in SharePoint transforms documents along with folders and libraries into permissions islands that bypass routine security controls. These items follow independent permission rules outside of site structure boundaries, thus becoming evasive during regular permission inspection processes.
Permission islands tend to grow in number during advanced environments since content moves numerous times following reorganizations or migrations. Multiple content movements and copies, and organization changes increase the chance of broken inheritance, which causes an expanding network of permissions that violate the security design. The growing number of permission islands creates challenges for conducting complete security assessments during environmental aging.
Research indicates that business SharePoint environments typically hold thousands of items featuring broken inheritance, but most of these items lack proper monitoring and regular review. Manual identification of these permission anomalies proves to be a daunting task due to their massive scale, so specialized tools, along with proper approaches, are needed to track them properly.
Application Permissions and Service Accounts
The Microsoft 365 integrated application framework creates hidden permissions because it allows third-party applications to access the environment. Third-party applications use delegated permissions along with application permissions, which remain hidden when performing standard user access reviews. The increasing number of connections establishes multiple access points that do not necessarily follow organization security policies and governance guidelines.
Service accounts preserving their persistent access control have access to dormant accessible paths beyond their original expiration periods. Employees rarely question service accounts during review periods because ownership classification becomes uncertain as time progresses. Persistent unmanaged service accounts transform into security risks because they retain extensive access permissions over several resources.
The survival of API connections between services after projects end enables them to establish hidden security gaps that violate defined security limits. API connections between applications generate complex permission routes that security reviews focused on users will not detect, so they become possible points of entry into secure environments.
How to Uncover Hidden Permissions
Hidden permissions are often the silent enablers of data leaks, privilege misuse, and regulatory risk, especially in large, distributed Microsoft environments. Simply relying on native tools is no longer enough. To truly uncover who has access to what (and how), organizations must take a deeper, multi-layered approach. Here’s how to get started:

Utilize Advanced Access Reports
Native tools from Microsoft show basic permission traces, while users need extra capabilities to locate all inaccessible paths. The audit reports from SharePoint Admin Center deliver basic informational value, but cannot discover all permission inconsistencies across the entire environment. Reports by Microsoft tend to show only direct permissions without presenting detailed access maps that incorporate complete potential access points.
The execution of custom PowerShell scripts gives organizations greater visibility when detecting broken inheritance in their environmental assets. The scripts perform structured permission checks by evaluating parent-child structures to track down inheritance damage spots. The systematic automation of this process enables organizations to perform continuous scanning of their whole environment to locate permission issues that people would miss.
Organizations benefit from third-party permission analysis solutions, which reveal complete information about intricate permission arrangements that baseline monitoring systems overlook. Specialized algorithms formed part of these solutions, which specialize in detecting permission inconsistencies alongside unusual access patterns as well as security risks. Companies with extended Microsoft 365 environments gain major visibility into access controls and an enhanced security position from these specialized tools.
Conduct Regular Permission Audits
A regular auditing program will enable organizations to find permission issues before they become critical. Healthcare organizations should audit high-value content areas monthly to verify that proper access restrictions remain effective for sensitive information. Organizations should begin their security work by monitoring critical business content and sensitive compliance areas because these are locations that yield maximum security impact.
Extended permission reviews of collaboration spaces during each quarter help organizations find systematic permission problems that individual sites and libraries would not detect. The reviews need to examine group affiliations along with all sharing links and application rights to render accurate access information. Regular organizational permission reviews enable organizations to find and handle permission drift before severe security problems arise.
The review process after project completion checks existing access, which needs removal once the project reaches completion. Temporary permissions given for project-based work must be revoked when all tasks in a particular project finish. Organizations can reduce hidden permission problems when they carry out formal permission review procedures following project completion.
Implement Access Path Analysis
Standard permission reports fail to uncover access routes, which become visible when organizations use access path analysis to understand permissions. Organizations achieve full understanding of their true permission networks by monitoring all accessible methods to specific content through direct permissions, together with group membership and sharing link permissions. This allows them to establish actual security boundaries without assumptions.
The identification of full group membership structures reveals access pathways that cannot be identified through standard reports. Such an evaluation should examine both direct users along those in nested membership groups and dynamic access members activated through user criteria. Organizations that analyze these intricate relationships will discover permission routes that go undetected during individual site or document permission assessments.
Research on active sharing links enables organizations to find alternative access methods that circumvent core permission settings, particularly for shared resources without time restrictions. Alternative ways to access data exist through these links and potentially provide access to permissions even systems reports cannot detect. Organizations must track complete records of active sharing links to confirm alternative access methods adhere to their established security guidelines and governance standards.
Leverage Microsoft Purview for Broader Insights
The Microsoft Purview solution (formerly Microsoft 365 Compliance Center) enables firms to find possible permission problems across all their networks. The sensitive information type scanning tool enables organizations to direct their permission review activities toward at-risk data assets. Organizations can achieve the highest security impact through their permission remediation efforts by first identifying sensitive content locations.
Owned access review procedures allow standardized permission evaluation throughout the environment using documented approval processes and defined accountability arrangements. Structured reviews serve as a powerful tool that yields essential value to industries operating under strict regulations because they generate necessary documentation of access choices. Through Purview, organizations achieve enhanced security along with compliance documentation at the same time.
Activity monitoring detects unconventional access behaviors because they might uncover stray permission pathways. Organizations using this assessment method detect permission-related anomalies by comparing who obtains which content and their methods for obtaining it beyond basic static analysis. Organizations can attain a comprehensive security evaluation through the combination of behavioral analysis alongside their structural permission evaluations.
Best Practices for Managing Hidden Permissions
Hidden permissions can quietly expose your Microsoft 365 environment to serious security risks, often without your IT team even realizing it. Managing them effectively requires more than just reactive fixes. Below are key best practices organizations can implement to uncover and control these invisible access paths before they turn into full-blown security incidents.
1. Implement a Least-Privilege Model
Organizations must follow a proactive approach to least-privilege principles by implementing them through their entire Microsoft 365 environment rather than just responding to found hidden permissions. Organizations should automatically apply limited access permissions for all new sites and content when establishing security protocols for new content creation. The Adopted Method puts the responsibility on secure environment maintenance rather than demanding time on seeking and restricting improper permissions.
Departments must provide justification documents for elevation of access beyond regular roles to support auditing of permission modifications while preventing security issues that emerge from permission creep. Documentation serves as security documentation and delivers essential background information about previous permission choices to new administrators who lack understanding of those administrative decisions. In the extended permission expansion process, additional friction helps organizations grant permissions only when necessary.
The use of time limits on permissions provides automatic expiration of temporary permissions during their specified duration. The method delivers maximum security benefits, especially during project collaboration with contractors as well as temporary staff assignments. Organizations benefit significantly from establishing expiration as the standard approach rather than an exception since this practice greatly decreases the buildup of old permissions, which tend to create security problems.
2. Standardize Permission Structures
Standards-based permission approaches significantly minimize hidden permission issues since they establish straightforward access frameworks that organizations can track effectively. The implementation of standardized role-based access control models enables organizations to create consistent permission expectations that they can monitor and apply across all areas of their environment.
The allocation of clear ownership and permission management duties for every content section ensures proper responsibility for continuous permission management activities. Defined personnel or teams who handle permission responsibilities detect access drift before any harm can occur. Organizations must document the person in charge of content ownership assignments and evaluate them throughout the evolution of organizational structures.
Standard permission adjustments require guidance from documented inheritance patterns and exception process rules. The documentation establishes both security gaps and the administrator’s comprehension of the exception rationale. Organizations that handle permission exceptions through structured formal decisions instead of spontaneous adjustments preserve centralized management of their security borders.
3. Utilize Access Reviews and Recertification
Business requirements that change through time can be accommodated by regular validation processes, which maintain suitable access permissions. The review of sensitive content-area permissions occurs every quarter to verify these permissions stay relevant to the company’s demands alongside security protocols. Business operations need to be assessed by permission reviews as part of the analytical process.
The annual recertification process of all special access rights helps organizations identify and remove unneeded permissions that should have been removed. Organizations that need elevated permissions must provide an explicit confirmation showing their ongoing necessity, thus identifying unnecessary access rights for removal. The examination process stands vital for administrative permissions because these create the maximum potential security risks when improperly managed or granted.
Temporary permission expiration by automation systems occurs automatically when users do not renew their grants actively. The system requires active maintenance instead of dependent memory for removing access. The automated expiration system decreases permission sprawl across time when used for project-based collaboration and short-term contractor access.
4. Train Content Owners on Permission Best Practices
The source of many hidden permissions stems from user actions, which come from goodwill but a lack of knowledge during content sharing and management procedures. Organizations should provide easy-to-understand instructions about Microsoft 365 permission functionality, alongside inheritance understanding and sharing ramifications to build stronger security choices in content owners. Training must concentrate on demonstrating real-world scenarios rather than theoretical explanations because this improves the connection to regular operational choices.
Decision tree logic provides content owners with simple tools to decide proper content sharing methods according to sensitivity level and target audience, along with organizational regulations. The tools deliver explicit guidance during the time users make sharing choices, which replaces the need to remember compound security guidelines. Simplifying workflow-based permission decision-making helps organizations limit the occurrence of inappropriate sharing actions that lead to hidden access paths.
Strategies that supply real-time alerts about permission problems help users learn security best practices by applying them directly. Feedback delivered promptly about permission issues enables users to build better instinctive approaches to appropriate sharing decisions over time. Through continuous feedback, the organization builds an environment where its overall permission systems develop into stronger versions.
Tools for Addressing Hidden Permissions
Native Microsoft Solutions
The fundamental permissions visibility of SharePoint Admin Center, Microsoft Purview, along with the PowerShell solution, demands customized setups yet identifies insufficient hidden permission points. The built-in tools from Microsoft serve as fundamental permission management solutions, while users usually require additional custom scripts and third-party solutions to acquire full visibility across elaborate permission systems.
The built-in features of Microsoft for sensitivity labeling and information protection function to maintain uniform access control for delicate content, which decreases the possibility of unauthorized sharing that results in unknown permissions. Organizations can benefit from these features due to their ability to create additional safeguards that enhance basic permission controls, specifically for vital information that needs full-time defense regardless of current location.
Third-Party Governance Platforms
Specialized solutions operate with built-in permission analysis features that detect anomalies in Microsoft 365 environmental permissions. Permission analysis tools provide three key features that involve continuous comparison of permissions through time and advanced monitoring of uncommon access patterns, in addition to full-path permission mapping capabilities. Organizations possessing complex environments or requiring strict compliance standards benefit greatly from this tool, which expands their visibility into permissions alongside their control elements.
The platforms enable organizations to automatically detect and resolve hidden permissions through their built-in remediation systems while performing detection activities. Larger environments benefit a great deal when automated remediation tools execute permission-level tasks that would take excessive time to address through human intervention. Organizations can sustain proper permission hygiene because these tools provide both detection and correction features.
Security Monitoring Integration
Security Information and Event Management platforms achieve configuration success by detecting irregular access patterns that signal improper use of hidden permission access points. These systems monitor environmental access activities against pre-established baselines that help detect hidden permission misuse, which results in security incidents.
Through this approach, organizations can detect hidden permission problems through examination of what users do instead of their theoretical system rights. These systems track access events to discover security issues through user behaviors that go against typical engagement patterns and disruptive patterns in business activity.
How Lepide Helps
Lepide delivers comprehensive visibility and control over Microsoft 365 permissions, helping organizations uncover and remediate hidden access risks that native tools often miss. With Lepide Auditor, you can automatically scan your entire Microsoft 365 environment-including SharePoint, OneDrive, Teams, and Exchange Online-to identify who has access to what, where permissions have broken inheritance, and which users or groups have excessive or anomalous rights.
Conclusion
The security challenge posed by hidden permissions in Microsoft 365 affects organizations of all sizes but can be reasonably managed. Established governance practices combined with systematic discovery procedures and identity of permission origins allow organizations to maintain Microsoft 365 collaboration benefits while reducing security risks.
To create a complete permission management strategy, organizations should integrate their efforts with security technology platforms and defined procedural standards. Technological solutions’ visibility and automation capabilities enable organizations to search and repair hidden permissions throughout their systems at a large scale. Drivers and procedures create similar permission approaches throughout the organization, which sustain across evolving personnel groups. An organization’s security culture must promote proper access control to prevent new hidden permissions from forming because of regular user workflow.
Organizations that focus on proactive hidden permission detection gain improved Microsoft 365 collaboration alongside maintaining sufficient security measures required by data protection and compliance regulations. Such harmonious security strategies enable business value to thrive on Microsoft 365 platforms while building sustainable security practices that advance organizational goals.