There is nothing unusual in the growth of an Exchange database with the addition of data. As mailboxes are added, the database increases in size to accommodate them. And it is expected naturally that database size decreases as data is deleted. But one may be amazed to see some abnormalities here—no decrease in database size is observed as mailboxes are deleted from Exchange database. And one more surprise! After deleting some mailboxes, find the Exchange database size; now, add a few mailboxes to it, and again find the Exchange database size. The size of the Exchange database remains the same in both the situations! This puzzling situation is related to Exchange white space and this is how it works in Exchange database.
What is white space?
White space is the database storage area that has become available for storing new data because of the deletion of existing data. Exchange, instead of reducing the database size, makes this space available for the addition of new mailboxes. This reclaimed storage area is known as White space. Also, it is known by names such as available mailbox space, free space, and free database pages.
Let us do some real calculation…
It’s better to learn about white space through a real example. Imagine that you are deleting some mailboxes (6 GB data) from the Exchange database of size 24 GB. This is how white space comes in calculation:
|
Before data deletion Database size= 24 GB Space available for new data (without increasing database size) = 0 GB |
|
After data deletion Data deleted = 6 GB Expected database size = 24 – 6 = 18 GB> But, real database size = 24 GB Space available for new data (without increasing the database size) = 6 GB |
|
Inference Database size after deletion = 24 GB = Database size before deletion Space available for new data (without increasing the database size) = 6 GB = white space |
How to find white space?
There are two ways to find the white space:
- from Windows application event log
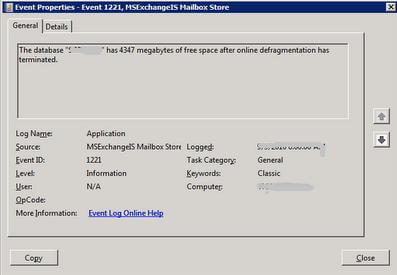
Event ID 1221 in the Windows application event log provides the amount of white space in Exchange versions up to 2007. However the value given by event ID 1221 is a conservative estimate only. You can note it as:
Event: 1221
Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox StoreType: Information
Category: General
Description: The database “<storage_group>\<mailbox_store> (<server_name>)” has <nnn> megabytes of free space after online defragmentation has terminated.
- using Database Space Tree Dump (Eseutil/ms)
Exchange Server Database Utility space dump (Eseutil/ms) provides a better estimate of the whitespace.
Defragmentation – For managing the whitespace in the Exchange database
White space in Exchange database is effectively managed through database defragmentation. It is of two types—online and offline.
Online database defragmentation
Online defragmentation is automatic. It is done on every night to recover the disk space. However, the database size remains the same even after the online defragmentation. To reduce the size of Exchange database, you need to perform offline defragmentation.
Offline database defragmentation
Offline defragmentation reduces database size and compacts it by the elimination of unused storage space. Defragmentation actually is the creation of a new database having no empty pages, and the subsequent replacement of the older one with the new one. The older one will be deleted or moved.
Offline defragmentation is done using the Eseutil facility. Please remember that defragmentation may not yield considerable free disk space unless there is a heavy deletion or moving of data. Though the defragmentation improves the performance of the Exchange database, it is not recommended regularly; it is recommended only when there is a need to reclaim large amount of space.
How to performing offline defragmentation in Exchange 2000/2003?
Before staring the offline defragmentation, ensure that free space is more than the size of the database (at least 110%). Also, at a time, run the command only on one database.
- In Exchange System Manager, right-click the information store and click Dismount Store.
- Enter cd Exchsrvr\Bin in the command prompt.
- Enter eseutil /d in the command prompt.
- Enter a database switch and the options required.
When to perform offline defragmentation?
Experts suggest offline defragmentation:
- when there is a scarcity of storage space
- when a large amount of white space (more than 30% )is there, and no considerable amount data is there to be added in recent future
- when defragmentation alerts are logged in the application log
- when there are issues or errors to be solved through offline defragmentation
- when it is necessary to mount the database (when the database size limited is reached)
- after a hard repair(eseutil /p)
- to improve the performance of Exchange database
Note:
- No need to run offline defragmentation regularly as online defragmentation is done by Exchange every night.
- Do not do offline defragmentation when the database has some inconsistently issues.
What after defragmentation?
It is recommended to perform a full (online) database backup after defragmentation as there is a re-arrangement of data during defragmentation.
Exchange Health Monitoring
Exchange health monitoring is a term coined to refer the monitoring of Exchange Server aspects like Server Availability, CPU and Memory Usage, Mailbox Database Usage, Mailbox Queue, etc. Professional auditing solutions like Lepide Auditor Suite helps Exchange administrators in performing effective Exchange health monitoring.
Blog Summary
The storage space reclaimed by the deletion of data is reserved for the addition of new data in Exchange database. So there is no apparent reduction in the size of the Exchange database. This reclaimed storage space is known as white space. White space in Exchange database is managed through a process known as defragmentation. To keep an eye on some other critical Exchange parameters, administrators can use professional solutions like Lepide Data Security Platform.
 Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration
Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration 15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them
15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them Why the AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
Why the AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
