
Understanding the fundamental building blocks of Active Directory is crucial for efficient management and organization within an IT infrastructure. In this blog, we delve into the concept of Organizational Units (OUs) in Active Directory, exploring their role as containers for organizing and managing objects such as users, groups, and computers, and how they streamline administrative tasks within a domain environment.
What is an OU in Active Directory?
In Active Directory, organizational units (OUs) serve as container objects that organize and administer network resources effectively. They allow for the grouping of resources based on common attributes such as location or purpose, mirroring real-world business hierarchies. By using OUs, administrators can implement targeted management policies, control access, and establish security restrictions for specific groups of objects. Moreover, OUs facilitate task delegation and control, enabling multiple administrators to manage different aspects of the network. The hierarchical structure of OUs, where they can be nested within each other, simplifies the management of large-scale networks with numerous resources. OUs also provide a means for applying group policies to specific sets of users and computers, further enhancing the efficiency of network management.
Benefits of Active Directory Organizational Units
Organizations require robust security measures to protect their IT infrastructure. Active Directory (AD) provides precise and accurate security controls to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It allows for the easy application of specific security controls to different objects using Organizational Units. By linking Group Policies (GPOs) to OUs, administrators can implement targeted settings for groups of users or devices. Additionally, AD facilitates easy delegation of administrative tasks, enabling the assignment of specific permissions to business users for OU management. For instance, helpdesk technicians can be granted the ability to reset passwords for all domain users or restricted to managing passwords for users within a specific child OU. This flexible approach streamlines administrative processes and strengthens security by ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to relevant data and resources.
How to Manage OUs using ADUC
Creating an OU
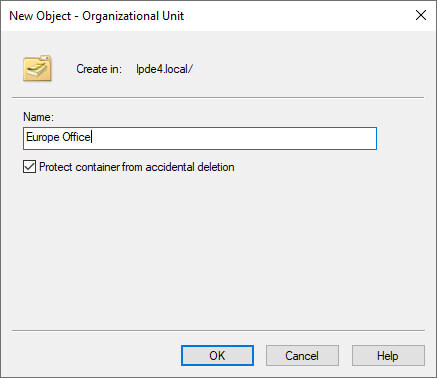
- Right-click the desired domain or OU in ADUC.
- Select “New” → “Organizational Unit.”
- Assign an appropriate name to the new OU.
- Click “OK” to create the OU.
Renaming an OU
- Right-click the OU to be renamed.
- Select “Rename.”
- Specify the new name.
Moving an OU
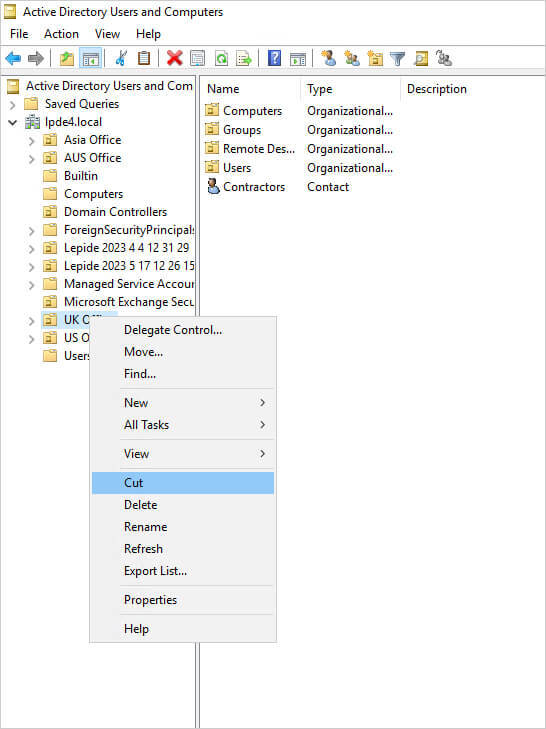
- Right-click the OU to be moved.
- Select “Cut.”
- Navigate to the target location and right-click.
- Select “Paste” to move the OU.
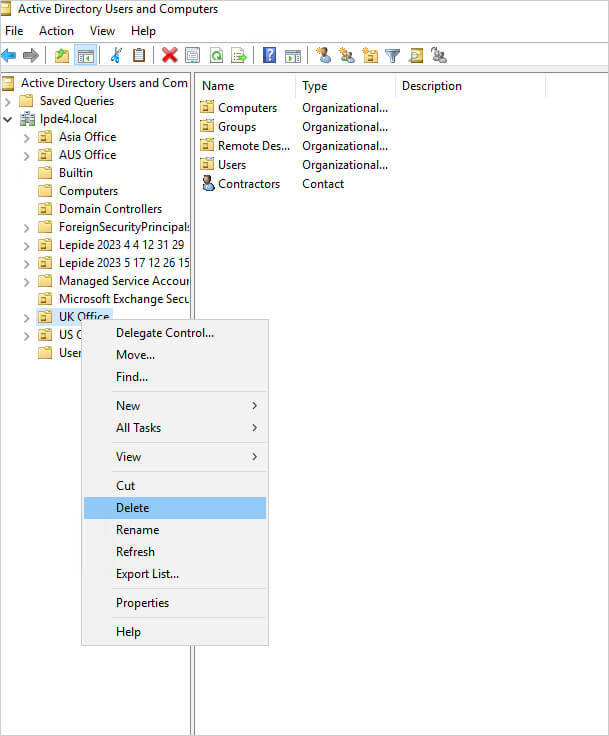
Deleting an OU
Caution: Deleting an OU will permanently remove all objects within it.
- Right-click the OU to be deleted.
- Select “Delete” to confirm the deletion.
Best Practices for Using Organizational Units (OUs)
Here are some best practices for using OUs effectively:
- Plan OUs Hierarchically: Design your OU structure to reflect your organization’s structure or business units. A hierarchical structure makes it easier to manage and delegate administrative tasks.
- Keep it Simple: Avoid creating too many OUs or nesting OUs too deeply. A complex OU structure can make administration more difficult and increase the risk of misconfiguration.
- Delegate Authority: Delegate administrative tasks by assigning permissions to OUs rather than individual objects. This allows you to distribute administrative responsibilities while maintaining centralized control.
- Group Similar Objects: Organize objects within OUs based on common characteristics or administrative requirements. For example, create separate OUs for different departments, geographic locations, or types of objects.
- Use Group Policy Objects (GPOs): Link GPOs to OUs to apply consistent policies and settings to objects within those OUs. This allows you to manage configuration settings centrally and apply them to specific groups of users or computers.
- Implement Security Groups: Use security groups in conjunction with OUs to control access permissions more effectively. Place users and computers into security groups and then assign permissions to those groups at the OU level.
- Consider Lifecycle Management: Plan your OU structure with the object lifecycle in mind. For example, create separate OUs for new hires, temporary employees, and terminated users to simplify management and ensure proper access control.
- Document Your Structure: Maintain documentation that outlines your OU structure, including the purpose of each OU and any associated policies or permissions. This documentation helps ensure consistency and provides guidance for future administrators.
- Regularly Review and Refine: Periodically review your OU structure to ensure it remains aligned with your organization’s needs and objectives. Make adjustments as necessary to accommodate changes in your environment or business requirements.
- Test Changes Before Implementation: Before making significant changes to your OU structure or applying new policies, test them in a controlled environment to identify any potential issues or conflicts.
By following these best practices, you can create an OU structure that facilitates efficient administration, enhances security, and supports the overall management of your Active Directory environment.
Auditing OUs in Active Directory with Lepide
In large enterprises, the built-in Active Directory auditing capabilities can overwhelm IT teams with large amounts of noise, making it laborious to identify specific events. Lepide Active Directory Auditor streamlines this process by auditing all Active Directory modifications. Our software will enable you to:
- Uncover potential risks and vulnerabilities
- Track and identify common attack vectors
- Detect and respond to malicious activities in real-time
- Manage Active Directory security and compliance from a centralized platform
Lepide’s preconfigured reports enable you to investigate security incidents in-depth by generating a comprehensive audit trail. To enhance monitoring, you can set up real-time alerts that will be delivered directly to your inbox or mobile device via the Lepide Mobile App.
If you’d like to see how Lepide Auditor can help you monitor OUs in Active Directory, start your free trial today.
 Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration
Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration 15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them
15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them Why the AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
Why the AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
